Achieving ESG Reporting Maturity Through Better Data Management
Sustainability reporting is evolving rapidly across Europe, and soon, Chief Sustainability Officers, CFOs, and ESG managers will need to handle far more than a handful of KPIs in spreadsheets. What was once simple is becoming a complex web of metrics spanning supply chains, finance, operations, and HR.
Expectations from investors, regulators, and employees are rising. In this environment, the credibility of ESG reporting depends on one thing above all: data maturity.
Understanding ESG Data Maturity for Reliable Reporting and CSRD Compliance
Reaching credible disclosures isn’t about producing a glossy PDF at year-end. It’s about whether your data is accurate, traceable, and up to date when auditors or investors come knocking.
Most organisations start with scattered spreadsheets, annual data calls, and unclear ownership. But maturity is a journey. At the other end of the spectrum, leaders embed automated collection, continuous updates, and enterprise-wide transparency, giving boards and regulators confidence in every figure reported.
ESG Data Management Maturity Model: A Roadmap to Credible Sustainability Reporting
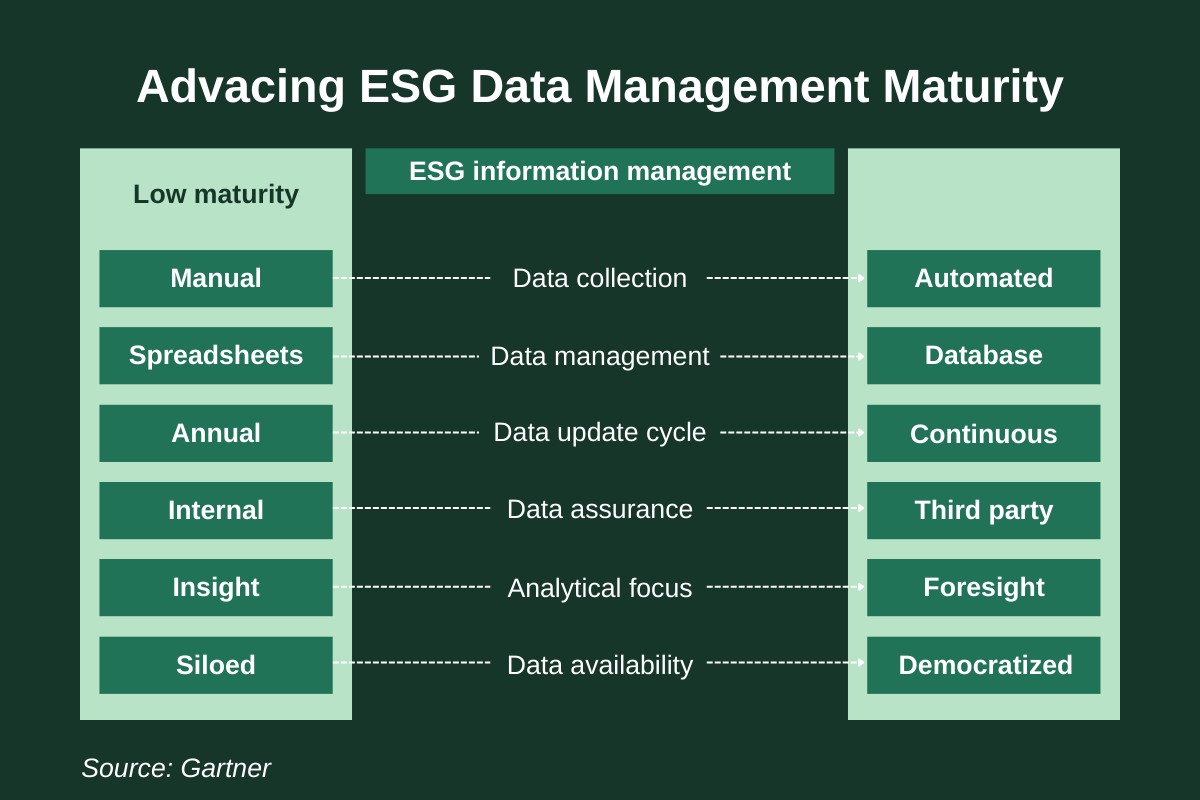
Gartner’s Advancing ESG Data Management Maturity model provides a practical roadmap for advancing ESG data management maturity. It outlines how organisations move from fragmented, manual reporting towards a fully integrated system that underpins decision-making.
Six dimensions show what progress looks like and why it matters:
Data Collection – From manual spreadsheets to automated capture embedded in operations.
Data Management – From scattered files to structured databases with governance and audit trails.
Data Update Cycle – From annual calls to rolling, near-real-time dashboards.
Data Assurance – From ad hoc validation to embedded controls and independent verification.
Analytical Focus – From reporting hindsight to predictive foresight and scenario planning.
Data Availability – From siloed specialists to democratized access across the enterprise.
Each stage brings you closer to credible reporting that meets CSRD’s assurance and transparency requirements. Below, we explore each dimension in more detail:
1. Data Collection
At the earliest stage, sustainability data is often gathered manually, typically through emails and disconnected spreadsheets.
The effort is heavy, errors are common, and no one is quite sure who owns which figures.
Mature organisations, by contrast, embed collection directly into operational systems.
Information flows automatically into a single source of truth, supported by controls that check completeness and accuracy without slowing the pace of work.
2. Data Management
Immature reporting environments scatter metrics across teams, each with its own files and calculation methods. There is little version control, and reconciling figures becomes a project in itself.
As capability grows, data is housed in structured databases with shared definitions and transparent governance. Permissions and audit trails maintain high standards while creating collaboration.
3. Data Update Cycle
When reporting relies on annual data calls, insights quickly become stale and emerging risks go unseen until it is too late to act. Advanced programmes replace one-off compilation with rolling updates. Dashboards refreshed in real or near-real time allow managers to monitor performance and adjust course long before the year-end narrative is written.
4. Data Assurance
In the early stages, validation is ad hoc and largely internal, leaving disclosures open to challenge. Mature organisations build documented controls and reconciliations into their process and invite independent assurance, whether from internal audit or external experts. This discipline strengthens credibility with boards, investors, and regulators alike.
5. Analytical Focus
Basic ESG reporting looks back, summarising results without explaining their strategic implications. At higher maturity, data becomes a lens for both foresight and hindsight. Scenario planning, predictive tools, and stress testing reveal how sustainability issues may impact enterprise value, supply chain resilience, or stakeholder expectations, enabling leadership to make more informed decisions.
6. Data Availability
In less developed settings, knowledge of sustainability remains confined to specialists, leaving colleagues and external partners with an incomplete understanding of the subject. As organisations progress, ESG information is treated as an enterprise asset. Role-based dashboards and secure portals open access to reliable evidence for people across functions and geographies. This transparency fosters accountability and turns data into a catalyst for collaboration and tangible impact.
Why It Matters for CSRD Compliance
The CSRD requires limited assurance of sustainability data starting in 2025. That means auditors must trace every figure back to its source. If your data resides in spreadsheets that are refreshed only once a year, credibility suffers.
Mature ESG data practices aren’t a “nice-to-have”; they are the foundation for CSRD compliance and the trust of your stakeholders.
Getting Started with ESG Data Management
Building mature ESG data practices begins with understanding what matters and creating a reliable foundation.
Focus on three core areas to set yourself up for long-term success.
Anchor Your Work in Materiality
Begin with a Double Materiality Assessment to identify the sustainability topics that truly impact your business and matter most to stakeholders. This isn’t just a regulatory requirement; it clarifies priorities, guides strategy, and ensures your reporting focuses on what’s most significant.
Ensure Data Traceability
Transparency relies on evidence. Make it clear where every data point comes from, which figures are estimated, and how they are calculated. Tools like the Terra ESG Platform can help maintain a fully traceable record, enhancing credibility with investors and auditors while building internal confidence in decision-making.
Adopt Continuous Practices
Treat ESG data as a living asset, not a once-a-year exercise. Move toward automated collection, structured databases, and rolling performance reviews. Continuous monitoring, supported by tools like Terra ESG Platform’s Collaborate module, helps streamline stakeholder engagement, enhance workflow efficiency, and refine strategies before issues escalate.
How ESG Reporting Platforms Accelerate Data Maturity?
Sustainability leaders can no longer rely on scattered spreadsheets or manual workflows. A dedicated ESG reporting platform transforms data management from a compliance chore into a source of strategic advantage.
The Terra ESG Platform, built on Microsoft Cloud for Sustainability, is designed to move organisations up the maturity curve faster by:
Integrating multiple data sources (from finance, operations, and supply chain) into a single, structured model.
Applying consistent rules and governance to ensure every metric is calculated the same way, every time.
Maintaining full traceability with audit trails that simplify assurance and build trust with regulators and investors.
Automating updates and validations so sustainability data stays current, accurate, and ready for disclosure at any moment.
Democratising access through role-based dashboards that give CFOs, CSOs, and operational teams the same version of the truth.
With governance and automation embedded into everyday processes, compliance with CSRD becomes smoother and less resource-intensive. More importantly, leadership gains timely insights to anticipate risks, track performance, and turn ESG reporting into a driver of measurable impact.
Turning ESG Data into Actionable Impact
Achieving ESG data maturity is an ongoing journey, not a one-time project. By improving how sustainability information is collected, managed, and shared, organisations strengthen the credibility of their disclosures and make more informed decisions.
Solid data foundations, supported by robust reporting platforms, ensure ESG reporting goes beyond mere compliance, becoming a driver of meaningful and lasting impact.
Want to know where you stand? Terra Reporting runs quick ESG maturity workshops. Contact us to benchmark your current practices. Together, we’ll identify quick wins and show how the Terra ESG Platform helps turn data into clear, compliant, and actionable insights.